NHRI Communications

研究發展
中老年人血中維他命D與身體活動功能
Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and physical performance in older adults: A nationwide study in Taiwan
 人體主要經由飲食及陽光曝曬獲得維他命D。老年人因腸道吸收功能降低或行動不便,導致陽光曝曬減少,以及皮膚合成功能與肝腎代謝功能降低;因此,維他命D缺乏(血中25(OH)D濃度< 50 nmol/L)狀況甚為普遍,歐美國家老年人缺乏比例甚至可達將近100%。而位處亞熱帶的東南亞國家,維他命D缺乏比例亦不容小覷:馬來西亞依族群有12 –73%、印度91%、中國36%、韓國69 – 80%,亞洲國家中,只有日本表現較好,約5 – 18% (1)。台灣目前老年人維他命D建議攝取量為10 μg/d。據1999 – 2000的「台灣國民營養健康狀況變遷調查」,台灣老年人維他命D的實際攝取量約為6 – 7 μg/d (2)。維他命D被視為萬靈丹,幾乎所有疾病都與維他命D有關,一份報告指出,若能提高所有歐洲人血中維他命D濃度至100 nmol/L,則每年可減少因疾病產生之經濟負擔187,000萬歐元(3)。
人體主要經由飲食及陽光曝曬獲得維他命D。老年人因腸道吸收功能降低或行動不便,導致陽光曝曬減少,以及皮膚合成功能與肝腎代謝功能降低;因此,維他命D缺乏(血中25(OH)D濃度< 50 nmol/L)狀況甚為普遍,歐美國家老年人缺乏比例甚至可達將近100%。而位處亞熱帶的東南亞國家,維他命D缺乏比例亦不容小覷:馬來西亞依族群有12 –73%、印度91%、中國36%、韓國69 – 80%,亞洲國家中,只有日本表現較好,約5 – 18% (1)。台灣目前老年人維他命D建議攝取量為10 μg/d。據1999 – 2000的「台灣國民營養健康狀況變遷調查」,台灣老年人維他命D的實際攝取量約為6 – 7 μg/d (2)。維他命D被視為萬靈丹,幾乎所有疾病都與維他命D有關,一份報告指出,若能提高所有歐洲人血中維他命D濃度至100 nmol/L,則每年可減少因疾病產生之經濟負擔187,000萬歐元(3)。自2008年起,本院群體健康科學研究所熊昭所長、許志成副所長及所內同仁,於台灣北中南東7間合作醫院,共招募了5,664名社區中年齡55歲以上之中老年人,進行「台灣中老年健康因子及健康老化長期研究調查(The Healthy Aging Longitudinal Study in Taiwan,簡稱HALST)」。所有個案皆填寫一份包含健康狀況、生活型態、身體活動及飲食的問卷,進行一系列包含血壓、體重、身高、腰臀圍、認知功能及身體功能的測量,並採取血液及尿液檢體。所有個案並定期接受電話訪問,關心健康現況。HALST已於2013年完成第一波收樣,目前正進行第二波追蹤訪視。
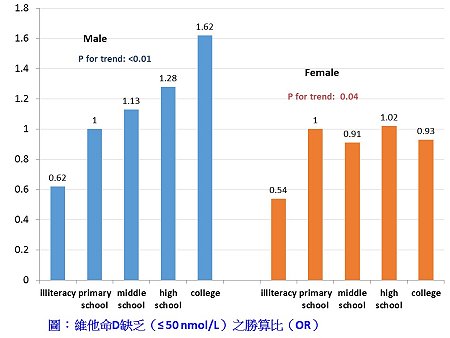
該所莊淑鈞助研究員與熊昭所長使用第一波收樣之問卷內容、血液檢體及身體活動功能評估結果進行維他命D與身體活動功能之橫斷性研究,結果顯示,22%男性與35%女性有維他命D缺乏現象,且維他命缺乏在高教育程度者、肥胖者、魚類及乳製品攝取量低者中較為明顯。大部分歐美的研究結果顯示,維他命D缺乏在教育程度低者較為普遍,而運動量(通常作為陽光曝曬的替代指標)越高,維他命低D缺乏的比例也較低。然而,莊博士研究則指出,教育程度越高,維他命D缺乏越普遍,而運動量則與維他命D缺乏無顯著相關,反而是務農工作等勞動量越高者,維他命D缺乏的比例也越低;推論應是教育程度高者,其生活型態上較少陽光接觸,或是因文化上對皮膚美白及防曬的重視,即使有運動,也是在室內或有重重的防曬措施之下。這現象,也許可解釋為何維他命D在該研究中與身體活動功能並無相關。運動,對減緩老年人身體活動功能的衰退有重要的角色,或許維他命D在身體活動功能上的重要性不及運動,但也有可能是第一波收案個案較健康,待第二波收案完成後,研究團隊就可進一步研究維他命D低者其身體活動功能的衰退是否會較快。另外,也有可能是嚴重維他命D缺乏才會影響到身體活動功能,本研究中嚴重維他命D缺乏(< 30 nmol/L):男性只有4人、女性34人,無檢測相關性的統計效力。
此研究結果已刊登於American Journal of Clinical Nutrition期刊線上版(4)。一般而言,經由陽光曝曬獲取維他命D的效率遠比營養補充品好(5),但陽光曝曬為雙面刃,國際上已有多篇文獻探討如何曝曬才能產生足夠維他命D(UVB)又不會引起皮膚癌(UVA)(the D-lemma),然目前多數研究集中在歐美國家白人。亞裔人口因膚色較深,維他命D合成效率不及白人。住在英國的白人,每週3次,約35%皮膚曝曬於中午的太陽9-16分鐘,有90%的人血中維他命D可達到50 nmol/L(6),但同住英國的孟加拉人,約需45分鐘的曝曬,但仍有25%的人未達50 nmol/L(7) 。目前台灣尚無相關研究。
參考資料:
- Palacios C, Gonzalez L. Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem? J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2014;144 Pt A138-145.
- Lee MS, Li HL, Hung TH, et al. Vitamin D intake and its food sources in Taiwanese. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2008;17(3):397-407.
- Grant WB, Cross HS, Garland CF, et al. Estimated benefit of increased vitamin D status in reducing the economic burden of disease in western Europe. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2009;99(2-3):104-113.
- Chuang SC, Chen HL, Tseng WT, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D and physical performance in older adults: a nationwide study in Taiwan. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(5):1334-1344.
- Ponda MP, Liang Y, Kim J, et al. Randomized clinical trial in vitamin D-deficient adults comparing replenishment with oral vitamin D3 with narrow-band UV type B light: effects on cholesterol and the transcriptional profiles of skin and blood. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017.
- Rhodes LE, Webb AR, Fraser HI, et al. Recommended summer sunlight exposure levels can produce sufficient (> or = 20 ng ml(-1)) but not the proposed optimal (> or = 32 ng ml(-1)) 25(OH)D levels at UK latitudes. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130(5):1411-1418.
- Farrar MD, Webb AR, Kift R, et al. Efficacy of a dose range of simulated sunlight exposures in raising vitamin D status in South Asian adults: implications for targeted guidance on sun exposure. Am J Clin Nutr. 2013;97(6):1210-1216.
《文/圖:群體健康科學研究所莊淑鈞助研究員》